A Comprehensive Guide to Jewelry 3D Printing Materials: Shaping the Future of Adornment
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Jewelry 3D Printing Materials: Shaping the Future of Adornment
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Jewelry 3D Printing Materials: Shaping the Future of Adornment. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Jewelry 3D Printing Materials: Shaping the Future of Adornment
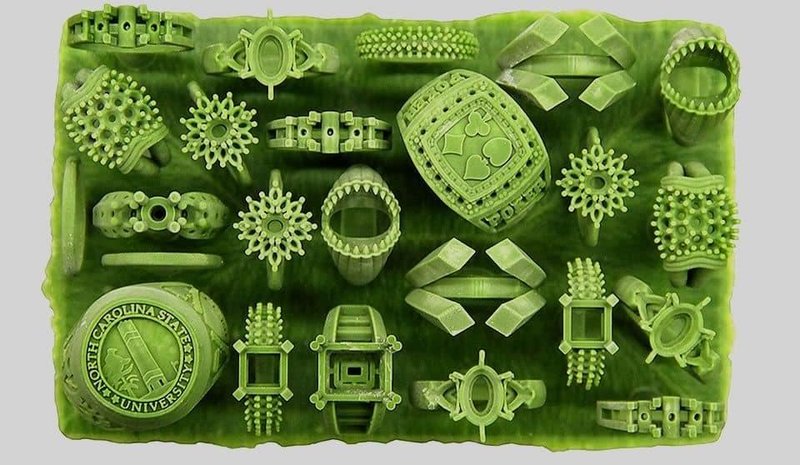
The jewelry industry is experiencing a transformative shift, driven by the emergence of 3D printing technology. This innovative approach offers unprecedented possibilities for crafting intricate designs, personalized creations, and cost-effective production. At the heart of this revolution lies the selection of appropriate 3D printing materials, each possessing unique properties that influence the final piece’s aesthetics, durability, and suitability for various applications.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse world of jewelry 3D printing materials, offering insights into their characteristics, advantages, and limitations. Understanding these materials empowers designers, jewelers, and enthusiasts to make informed decisions, bringing their creative visions to life with precision and finesse.
Exploring the Landscape of Jewelry 3D Printing Materials:
The realm of 3D printing materials for jewelry encompasses a wide array of options, each catering to specific design requirements and aesthetic preferences. These materials can be broadly categorized based on their composition and properties:
1. Metals:
-
Precious Metals:
-
Gold (Au): The epitome of luxury, gold is a highly sought-after material for jewelry. 3D printed gold jewelry offers intricate designs, intricate details, and a timeless elegance. However, the cost of gold can be a significant factor.
-
Silver (Ag): A more affordable alternative to gold, silver is known for its brilliance and versatility. 3D printed silver jewelry allows for complex geometries and intricate patterns, making it ideal for contemporary designs.
-
Platinum (Pt): Renowned for its durability and hypoallergenic properties, platinum is a favored choice for high-end jewelry. 3D printing enables the creation of unique platinum pieces with exceptional detail and longevity.
-
-
Base Metals:
-
Brass: A readily available and relatively inexpensive metal, brass offers excellent machinability and a warm, golden hue. 3D printed brass jewelry is often used for prototyping and creating statement pieces with a vintage aesthetic.
-
Bronze: Known for its rich patina and historical significance, bronze is a durable and aesthetically pleasing material for jewelry. 3D printing allows for intricate bronze designs, capturing the essence of ancient craftsmanship.
-
Stainless Steel: Renowned for its strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability, stainless steel is a versatile material for 3D printed jewelry. It offers a modern, sleek aesthetic and is suitable for both everyday wear and statement pieces.
-
2. Polymers:
-
Thermoplastics:
-
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): A robust and readily available thermoplastic, ABS is often used for prototyping and creating durable jewelry components. Its strength and ease of printing make it a versatile choice.
-
Polylactic Acid (PLA): A biodegradable and environmentally friendly thermoplastic, PLA is gaining popularity for its smooth finish and ease of printing. It is well-suited for delicate jewelry designs with intricate details.
-
Polycarbonate (PC): A high-impact, transparent thermoplastic, polycarbonate offers excellent durability and a polished finish. It is often used for creating unique and eye-catching jewelry pieces.
-
-
Elastomers:
-
Silicone: A flexible and durable elastomer, silicone offers a soft and comfortable feel. It is commonly used for creating 3D printed jewelry with intricate textures and organic shapes.
-
Rubber: A resilient and flexible material, rubber is often used for creating 3D printed jewelry with a distinctive tactile experience. It is well-suited for bold and statement pieces.
-
3. Ceramics:
-
Alumina: A strong and durable ceramic, alumina is often used for creating 3D printed jewelry with a sleek, polished finish. It is resistant to scratching and wear, making it a suitable material for everyday wear.
-
Zirconia: Known for its high strength and excellent biocompatibility, zirconia is used for creating durable and aesthetically pleasing jewelry pieces. Its white color and smooth finish make it a versatile choice.
4. Composites:
-
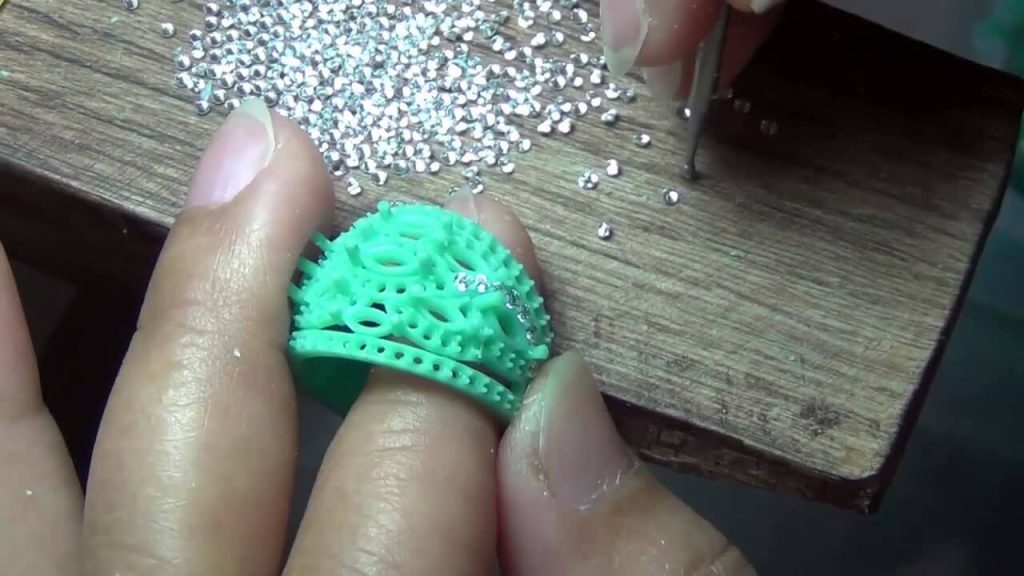
Resin: A popular choice for 3D printing jewelry, resin offers a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes. It is known for its high resolution and intricate detail capabilities.
-
Nylon: A strong and durable composite, nylon is often used for creating 3D printed jewelry with a matte finish. It is known for its resistance to wear and tear, making it suitable for everyday use.
5. Other Materials:
-
Wood: Natural wood can be incorporated into 3D printed jewelry, offering a unique and organic aesthetic. It is often used for creating statement pieces with a rustic charm.
-
Glass: While not typically used for direct 3D printing, glass can be incorporated into jewelry designs through casting or other techniques. It adds a touch of elegance and sophistication to the final piece.
Understanding the Advantages of Jewelry 3D Printing Materials:
The selection of appropriate 3D printing materials plays a crucial role in shaping the final characteristics of jewelry pieces. Each material offers unique advantages that cater to diverse design requirements and aesthetic preferences:
-
Design Freedom: 3D printing liberates designers from the constraints of traditional jewelry making techniques, allowing them to create intricate and complex designs with unparalleled precision.
-
Customization and Personalization: The ability to create unique and personalized pieces is a hallmark of 3D printed jewelry. This allows customers to express their individuality and create bespoke pieces that reflect their unique style.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: 3D printing eliminates the need for costly molds and tooling, making it a cost-effective solution for both small-scale and large-scale production.
-
Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing facilitates rapid prototyping, enabling designers to quickly iterate and refine their designs before committing to final production.
-
Sustainable Practices: 3D printing allows for the creation of jewelry with minimal waste, promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
-
Reduced Lead Times: 3D printing reduces lead times, allowing for quicker production and delivery of jewelry pieces.
-
Unique Textures and Finishes: 3D printing enables the creation of jewelry with intricate textures and unique finishes, adding depth and dimension to the final piece.
Navigating the Challenges of Jewelry 3D Printing Materials:
While 3D printing offers a plethora of advantages, certain challenges are associated with material selection and implementation:
-
Material Properties: Each 3D printing material possesses specific properties that influence its suitability for jewelry applications. Understanding these properties is crucial for choosing the right material for the desired aesthetic and functionality.
-
Post-Processing: Some 3D printed jewelry materials require post-processing steps, such as sanding, polishing, or finishing, to achieve the desired aesthetic and durability.
-
Durability and Wear Resistance: The durability and wear resistance of 3D printed jewelry can vary depending on the material used. Certain materials may be more susceptible to scratching, denting, or discoloration over time.
-
Material Availability: The availability of certain 3D printing materials can be limited, particularly for specialized or high-end applications.
-
Cost Considerations: The cost of 3D printing materials can vary significantly, impacting the overall cost of production.
-
Technical Expertise: A certain level of technical expertise is required to operate 3D printing equipment and to select and process appropriate materials.
FAQs: Demystifying Jewelry 3D Printing Materials:
1. What is the most popular 3D printing material for jewelry?
Resin is a popular choice for 3D printing jewelry due to its versatility, wide range of colors, and ability to create intricate details. However, the best material depends on the specific design requirements and aesthetic preferences.
2. Are 3D printed jewelry pieces durable?
The durability of 3D printed jewelry depends on the material used. Some materials, such as metals and ceramics, are known for their strength and durability, while others, such as plastics, may be more prone to scratches or wear.
3. How can I tell if a piece of jewelry is 3D printed?
It can be difficult to distinguish between 3D printed and traditionally made jewelry, especially with advanced printing techniques. However, some telltale signs include subtle inconsistencies in texture, small imperfections in the surface, or the presence of support structures.
4. Is 3D printed jewelry hypoallergenic?
The hypoallergenic properties of 3D printed jewelry depend on the material used. Some materials, such as platinum and titanium, are known for their hypoallergenic properties, while others, such as nickel, can cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
5. Can 3D printed jewelry be resized or repaired?
Resizing and repairing 3D printed jewelry can be challenging, depending on the material and design. Some materials, such as metals, can be re-melted and re-shaped, while others, such as plastics, may be more difficult to modify.
6. Is 3D printed jewelry ethical?
The ethical implications of 3D printed jewelry depend on the materials used, the manufacturing processes, and the overall environmental impact. Choosing materials sourced from sustainable and ethical suppliers is crucial.
Tips for Choosing the Right 3D Printing Material for Jewelry:
-
Consider the Design: The design of the jewelry piece will influence the choice of material. Intricate designs may require materials with high resolution and detail capabilities, while simple designs may be suitable for more affordable materials.
-
Think About the Aesthetics: The desired aesthetic will guide the choice of material. Metals offer a classic and elegant look, while plastics can provide a modern and vibrant aesthetic.
-
Evaluate the Durability: The intended use of the jewelry will determine the required level of durability. Everyday wear may require more robust materials, while statement pieces may be suitable for more delicate options.
-
Research Material Properties: Thoroughly research the properties of each material before making a decision. This includes understanding its strength, flexibility, finish, and hypoallergenic properties.
-
Consider Cost: The cost of materials will vary depending on the type and quantity used. Balance the desired aesthetics and functionality with the budget constraints.
Conclusion: The Future of Jewelry in the Age of 3D Printing
The integration of 3D printing technology is revolutionizing the jewelry industry, offering unprecedented possibilities for design, customization, and production. The careful selection of 3D printing materials is paramount to achieving the desired aesthetic, durability, and functionality for each piece.
As the field of 3D printing materials continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative and sustainable options to emerge, further shaping the future of jewelry and adorning the world with intricate and personalized creations. From precious metals to innovative composites, the possibilities are limitless, allowing designers, jewelers, and enthusiasts to push the boundaries of creativity and bring their visions to life with precision and artistry.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Jewelry 3D Printing Materials: Shaping the Future of Adornment. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
