A Glittering Timeline: Jewelry Art Through the Ages
Related Articles: A Glittering Timeline: Jewelry Art Through the Ages
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Glittering Timeline: Jewelry Art Through the Ages. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Glittering Timeline: Jewelry Art Through the Ages
Jewelry, a ubiquitous element of human adornment, transcends mere decoration. It embodies a rich tapestry of cultural expression, technological innovation, and artistic ingenuity, woven throughout history. From the earliest beads to intricate contemporary pieces, jewelry has served as a testament to human creativity, social status, and spiritual beliefs.
Ancient Origins: The Dawn of Adornment
The earliest forms of jewelry emerged during the Paleolithic era, with simple beads crafted from natural materials like shells, bones, and teeth. These adornments likely served both practical and symbolic purposes, signifying social status, tribal affiliation, or spiritual beliefs.
The Rise of Metalworking: A New Era of Sophistication
The advent of metalworking in the Neolithic period ushered in a new era of jewelry artistry. The discovery of copper, bronze, and gold allowed for the creation of more intricate designs, including pendants, rings, and bracelets. In ancient Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley Civilization, jewelry became increasingly elaborate, reflecting the growing wealth and power of their respective societies.
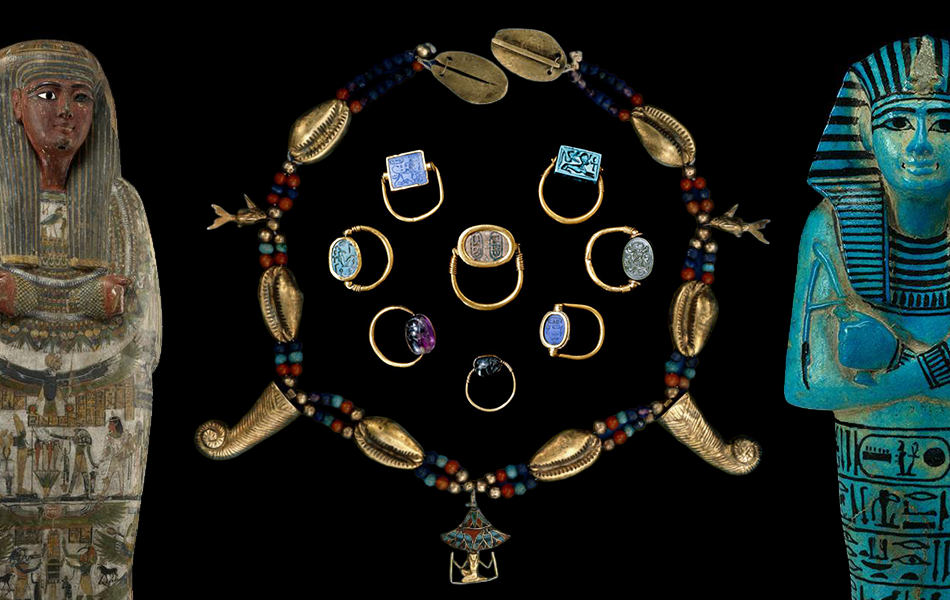
Ancient Egypt: Gold, Glamour, and the Afterlife
Ancient Egypt, with its fascination with the afterlife, produced some of the most iconic jewelry in history. Gold, a precious metal symbolizing the sun god Ra, was extensively used in intricate amulets, scarabs, and necklaces. These adornments were not merely decorative; they were believed to protect the wearer in this life and the next. The famous Tutankhamun’s tomb revealed a treasure trove of exquisite jewelry, offering a glimpse into the splendor of Egyptian craftsmanship.
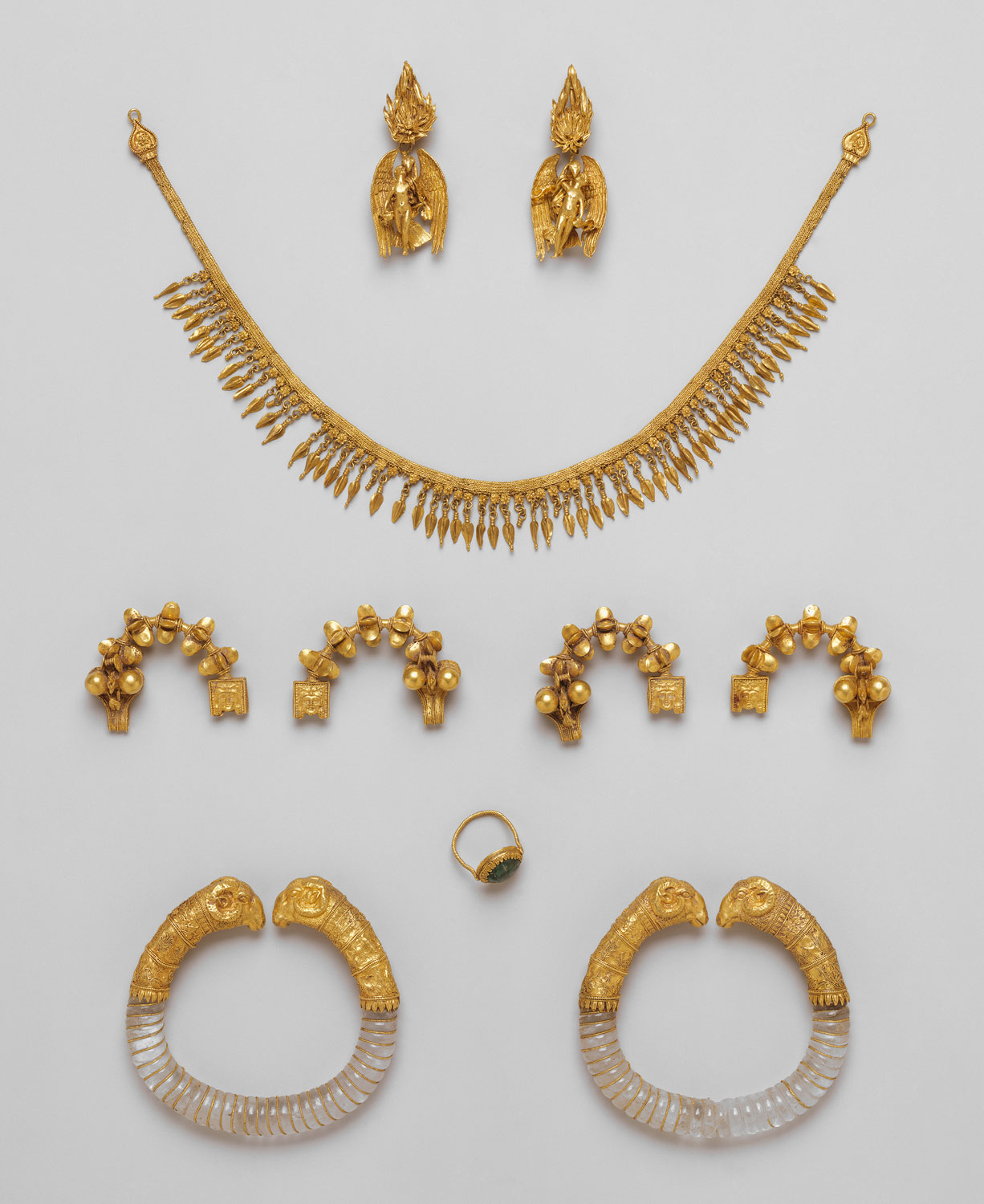
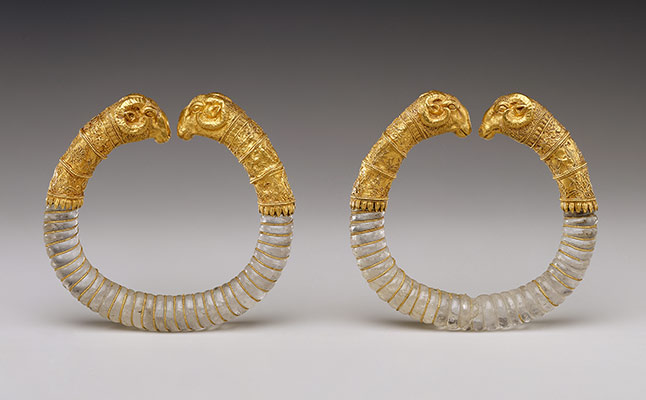
The Greeks and Romans: Classic Elegance and Symbolic Design
Ancient Greek and Roman civilizations further refined jewelry art, incorporating intricate patterns, mythological motifs, and gemstones. The Greeks, known for their love of beauty and symmetry, crafted elegant necklaces, earrings, and rings, often adorned with intricate filigree work and precious stones. The Romans, known for their practicality and grandeur, created robust pieces with bold designs, including elaborate brooches and fibulae.
The Middle Ages: Religious Devotion and Artistic Flourishing
The Middle Ages witnessed a surge in religious symbolism within jewelry. The rise of Christianity led to the widespread use of crosses, crucifixes, and other religious motifs in jewelry. This period also saw the development of cloisonné, a technique using thin metal strips to create compartments filled with enamel. During this time, the Byzantine Empire, with its rich artistic heritage, produced exquisite jewelry featuring intricate mosaics and gemstones.
The Renaissance: A Rebirth of Artistic Exploration
The Renaissance, a period of artistic and intellectual rebirth, saw a renewed interest in classical aesthetics. Jewelry became more elaborate and intricate, incorporating Renaissance motifs like human figures, mythological creatures, and floral patterns. The use of gemstones, particularly diamonds, became increasingly popular, reflecting the growing wealth and status of the upper classes.
The Baroque and Rococo Eras: Opulence and Grandiosity
The Baroque and Rococo periods were characterized by an explosion of opulence and grandeur. Jewelry reflected this trend, becoming increasingly extravagant and flamboyant. Large, ornate pieces, adorned with elaborate carvings, precious stones, and pearls, were the hallmark of this era. The French court, known for its lavish lifestyle, played a pivotal role in popularizing this style.
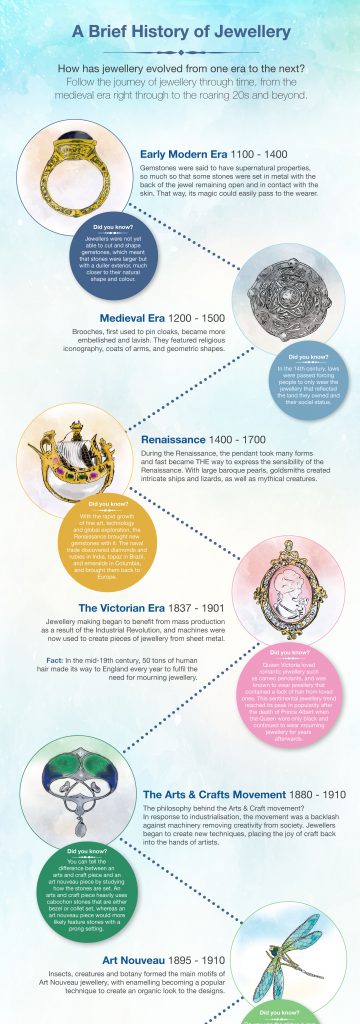
The Victorian Era: Sentimentality and Mourning Jewelry
The Victorian era, known for its sentimentality and mourning rituals, saw a shift in jewelry design. Jewelry became more personal and meaningful, often incorporating sentimental motifs like flowers, hair, and miniature portraits. Mourning jewelry, a somber yet beautiful expression of grief, was particularly prevalent during this time.
The Art Nouveau and Art Deco Movements: Artistic Innovation and Geometric Designs
The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed the emergence of two influential artistic movements: Art Nouveau and Art Deco. Art Nouveau jewelry, inspired by nature, featured flowing lines, organic shapes, and colorful gemstones. Art Deco jewelry, on the other hand, embraced geometric patterns, bold colors, and geometric shapes, reflecting the modern spirit of the era.
Contemporary Jewelry: A Fusion of Tradition and Innovation
Contemporary jewelry art continues to evolve, embracing a wide range of styles and techniques. From minimalist designs to avant-garde creations, contemporary jewelry reflects the diverse artistic sensibilities of the 21st century. Artists experiment with new materials, techniques, and concepts, blurring the lines between art and wearable objects.
Beyond Decoration: The Significance of Jewelry Art
Jewelry art, throughout its long history, has served as a powerful tool of communication, expressing individual identity, cultural heritage, and social status. It has played a significant role in shaping social norms, reflecting changing trends, and documenting historical events.
Cultural Significance:
- Social Status: Jewelry has historically served as a marker of wealth, power, and social standing. From the elaborate gold ornaments worn by ancient Egyptian pharaohs to the diamond tiaras of European royalty, jewelry has been a symbol of privilege and distinction.
- Religious Beliefs: Jewelry has been deeply intertwined with religious beliefs and practices throughout history. Amulets, talismans, and devotional pieces have been worn for protection, good luck, and spiritual guidance.
- Tribal Identity: Jewelry plays a crucial role in tribal cultures, signifying lineage, clan affiliation, and social roles. Traditional jewelry designs often incorporate unique motifs and symbols that reflect the specific cultural heritage of a particular tribe.
Artistic Innovation:
- Technological Advancement: The evolution of jewelry art has been closely linked to technological advancements. From the early use of simple tools to the sophisticated techniques of today, technological innovation has opened up new possibilities for jewelry design and craftsmanship.
- Material Exploration: Jewelry artists have continually explored new materials, from precious metals and gemstones to natural materials like wood, bone, and shells. This experimentation has led to a diverse range of textures, colors, and aesthetic effects.
- Artistic Expression: Jewelry art provides a unique platform for artistic expression, allowing artists to communicate their ideas, emotions, and perspectives through the medium of adornment.
Historical Significance:
- Time Capsule of History: Jewelry, as a durable and often treasured object, serves as a valuable source of historical information. Archaeological discoveries of ancient jewelry offer insights into past cultures, societies, and technological advancements.
- Social Commentary: Jewelry art has often been used as a form of social commentary, reflecting contemporary issues and challenging societal norms. From the feminist jewelry of the 1970s to the protest jewelry of the 21st century, jewelry has been a powerful tool for raising awareness and promoting social change.
Benefits of Jewelry Art:
- Aesthetic Appreciation: Jewelry art offers a unique opportunity to appreciate beauty and artistry in a tangible form. The intricate designs, craftsmanship, and use of materials in jewelry can evoke a sense of wonder and delight.
- Cultural Understanding: Studying jewelry art provides valuable insights into different cultures, their beliefs, values, and traditions. It helps us understand the significance of adornment in human societies and the role it plays in shaping our identities.
- Artistic Inspiration: Jewelry art serves as a source of inspiration for artists in various disciplines. The creativity, craftsmanship, and innovative techniques employed in jewelry design can inspire new ideas and approaches in other art forms.
FAQs on Jewelry Art Through the Ages:
Q: What are the earliest forms of jewelry?
A: The earliest forms of jewelry date back to the Paleolithic era and consisted of simple beads made from natural materials like shells, bones, and teeth.
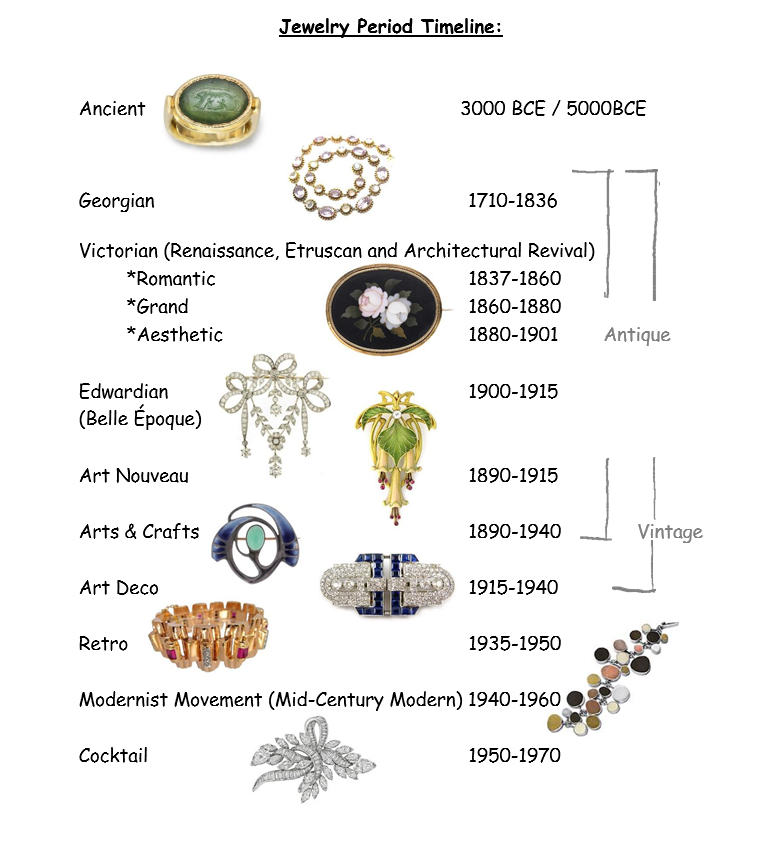
Q: What are some of the most significant periods in jewelry history?
A: Some of the most significant periods in jewelry history include Ancient Egypt, the Greek and Roman periods, the Middle Ages, the Renaissance, the Baroque and Rococo eras, the Victorian era, and the Art Nouveau and Art Deco movements.
Q: What are the main types of jewelry?
A: The main types of jewelry include necklaces, earrings, bracelets, rings, brooches, pendants, and amulets.
Q: What are the most common materials used in jewelry?
A: The most common materials used in jewelry include gold, silver, platinum, diamonds, pearls, gemstones, and various natural materials.
Q: What are some of the key techniques used in jewelry making?
A: Key techniques used in jewelry making include casting, soldering, engraving, setting, enameling, and filigree work.
Q: How does jewelry art reflect social and cultural changes?
A: Jewelry art reflects social and cultural changes by incorporating new materials, designs, and techniques. It also reflects changing trends in fashion, beliefs, and values.
Q: What are some of the contemporary trends in jewelry art?
A: Contemporary trends in jewelry art include minimalist designs, avant-garde creations, the use of unconventional materials, and the fusion of traditional and modern techniques.
Tips for Appreciating Jewelry Art:
- Explore Museums and Galleries: Visit museums and galleries that showcase jewelry art from different periods and cultures.
- Attend Jewelry Shows and Exhibitions: Attend jewelry shows and exhibitions to see the latest trends and innovations in jewelry design.
- Learn about Jewelry History: Read books and articles about the history of jewelry art to gain a deeper understanding of its significance and evolution.
- Appreciate the Craftsmanship: Take the time to examine the intricate details, craftsmanship, and materials used in jewelry.
- Consider the Context: When viewing jewelry art, consider the historical, cultural, and social context in which it was created.
Conclusion:
Jewelry art, a vibrant and enduring art form, offers a captivating glimpse into the history of human civilization. From the earliest beads to contemporary creations, jewelry has served as a testament to our ingenuity, creativity, and enduring fascination with beauty and adornment. By exploring the rich tapestry of jewelry art through the ages, we gain a deeper understanding of our cultural heritage, artistic evolution, and the enduring human desire to express ourselves through the language of adornment.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Glittering Timeline: Jewelry Art Through the Ages. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!